This study aimed to identify the effect of anti-gravity treadmill training on isokinetic lower-limb muscle strength and muscle activities in patients surgically treated for a hip fracture. A total of 34 participants were randomly assigned into two groups: anti-gravity treadmill training group and control group. The isokinetic muscle strength and endurance of hip flexor and extensor and the activities of the vastus lateralis , vastus medialis , gluteus maximus, and gluteus medialis muscles were measured before and after 4 weeks of the interventions.Significant improvements were observed in isokinetic muscle strength and endurance of hip flexors and extensors in both groups; however, no significant differences were observed between the groups except for muscle strength of the hip extensor. Statistically significant increases in the muscle activity of VL, VM, GM, and Gm were found before and after the intervention , and significant differences in muscle activities of GM and Gm were observed between the groups. Our results indicate that both groups showed improvement in muscle strength, endurance, and activities after the intervention. Additionally, anti-gravity treadmill training improved significantly more muscle strength at 60◦/s of the hip extensor and gluteus muscle activities than conventional therapy, which may be appropriate for patients with hip fracture surgery.
Article cited in:Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8572
Article link:https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33227913/
Approximately 1.35 million people die annually in road traffic crashes, and millions more suffer from injuries caused by that. Of patients injured in a road traffic crash, around 19–35.4% have femoral fractures. Femoral fractures occur as a result of relatively strong forces in events such as falls and traffic accidents, because of the specificity of the anatomical structure of the femur bone. Recently, the frequency of fractures has increased owing to the increase in traffic accidents in modern society involving even younger adults. Body weight is a crucial factor when standing upright or when walking, and the quadriceps muscle plays an important role in providing stability to the knee joint.
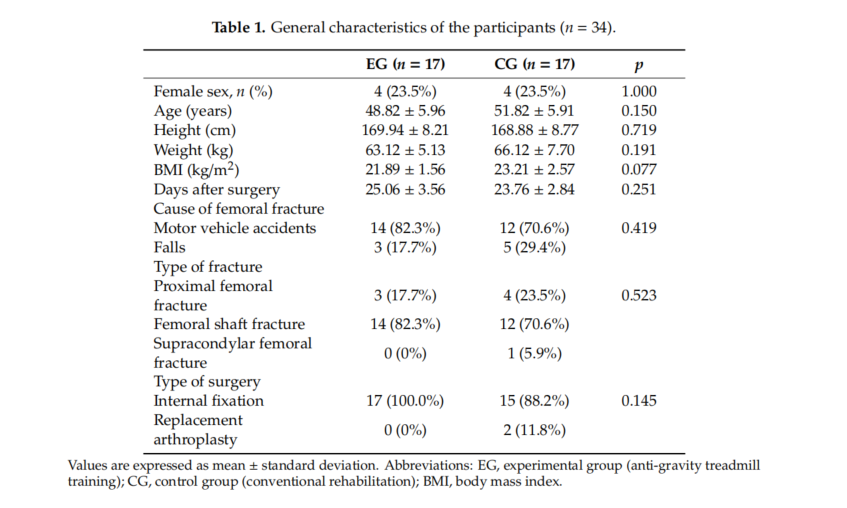
Therefore, the purpose of the present study was to investigate the effect of a rehabilitation training program using an anti-gravity treadmill on the strength and activity of lower-extremity muscles in patients surgically treated for a hip fracture.
In conclusion, both groups showed improvement in muscle strength, endurance, and activities after the intervention. Additionally, anti-gravity treadmill training improved significantly more muscle strength at 60◦/s of hip extensor and gluteus muscle activities than conventional therapy. Therefore, anti-gravity treadmill training compensates for the shortcomings of the conventional intervention used in rehabilitation and offers a rehabilitation protocol for a stable and effective gait in patients with a femoral fracture.