Key words: Stroke · Aerobic exercises · Antigravity treadmill exercise · Underwater walking exercise
Research background: Aerobic exercise training after stroke has positive efects on quality of life, motor recovery, and aerobic endurance. The aim of this study was to investigate the efectiveness of anti-gravity treadmill gait training and underwater walking therapy on cardiorespiratory ftness, gait and balance in stroke survivors.
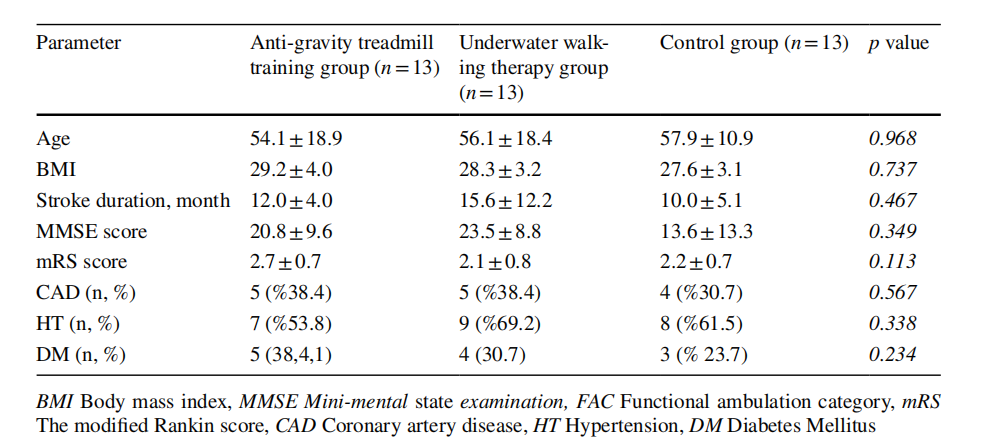
Research Methods:The study included 39 patients with a history of stroke who were admitted to our center between July 2017 and January 2018. The patients were randomly assigned to anti-gravity treadmill training, underwater walking therapy, or a control group. The aerobic capacity of the participants was evaluated with the 6-min walk test and cycle ergometer testing before and after the treatment. Balance was examined using the Berg Balance Scale (BBS).
Research Results:There was a statistically signifcant increase from pre- to post-treatment with regard to maximum heart rate and length of walking distance during 6-min walk test parameters in patients who underwent anti-gravity treadmill training (p<). The cycle ergometer training results showed signifcant improvements compared to baseline after treatment in patients who underwent anti-gravity training in terms of maximum heart rate attained during exercise stress testing, time to complete the test, rates of metabolic equivalents of task scores and peak oxygen consumption (p<0.05). Improvements were also observed in ventricular repolarization indices including corrected QT intervals (QTc), Tp-e interval and Tp-e/QT, Tp-e/QTc ratio in the anti-gravity group (p<0.05). BBS results showed no statistically signifcant diference in all groups (p>0.05).<
Conclusion: Anti-gravity treadmill training has favorable efects on cardiorespiratory ftness in stroke survivors.
The article is quoted in:Acta Neurologica Belgica (2023) 123:423–432
Abstract.:Acute stroke is defned as the acute onset of focal neurological fndings in a vascular territory as a result of impaired blood fow. This condition is the primary cause of disability worldwide and the second leading cause of death among patients aged ≥ 60 years . Stroke is also the third leading cause of mortality in developed countries.

Based On:A total of 70 consecutive patients with a history of stroke who were admitted to a tertiary level rehabilitation center between July 2017 and January 2018 were identifed for prospective analysis. Patients who were incompatible with the physiotherapy program due to functional status (n=31) were excluded, leaving 39 patients for evaluation (Fig. 1). The subjects participating in the study were randomly assigned to one of three groups using the sealed envelope method. All patients met the criteria for the World Health Organization (WHO) cerebrovascular disorders clinical and research classifcation . Approval was obtained from the Local Ethics Committee (TUEK 05.07.2017 / E-17–1396, ClinicalTrials. gov ID: NCT05058586) and informed consent of all participants was taken.
Before and after the treatment, the functional status of the patients was evaluated using the Barthel Index (BI), and balance and gait performance using the Berg Balance Scale (BBS). The BBS is a 14-item scale designed to assess balance and fall risk in adults. Each item is scored between 0 and 4, providing a possible maximum score of 56. Scores between 0 and 20 indicate that the balance is unstable, 21–40 that the balance is acceptable, and 41–56 that the balance is good . The BI is a 10-item scale that is widely used in cases with functional disability and is used to measure the performance of an individual in activities of daily living. While the maximum score is 100, a score of 0–20 indicates complete dependence, 21–61 severe dependence, 62–90 moderate dependence, 91–99 mild dependence, and a score of 100 indicates complete independence[12]
In conclusion, anti-gravity treadmill training was seen to have positive efects on aerobic capacity and functional status in stroke patients. In addition, a strong association was observed between anti-gravity treadmill training and improvements in ventricular repolarization heterogeneity. Due to the favorable efects of anti-gravity treadmill training on several parameters, this method may be used more frequently in daily practice.