Application in rehabilitation therapy
Abstract:
Objective: To explore the application value of anti-gravity treadmill training in the rehabilitation treatment of femoral shaft fracture after compression plate screw internal fixation. Methods: A total of 58 patients with femoral shaft fracture who underwent compression plate screw internal fixation 4 weeks after surgery were randomly divided into a conventional rehabilitation group and a combined rehabilitation group, with 29 cases in each group. The conventional rehabilitation group received rehabilitation treatment with manipulation, exercise therapy and physical therapy, while the combined rehabilitation group received anti-gravity treadmill training on the basis of the intervention measures of the conventional rehabilitation group; both groups received treatment 5 times a week, 20 minutes each time, for a total of 4 weeks.
The article is cited in:
Effect of anti-gravity treadmill on balance ability in patients with acute osteoporosis after surgery for knee joint rehabilitation
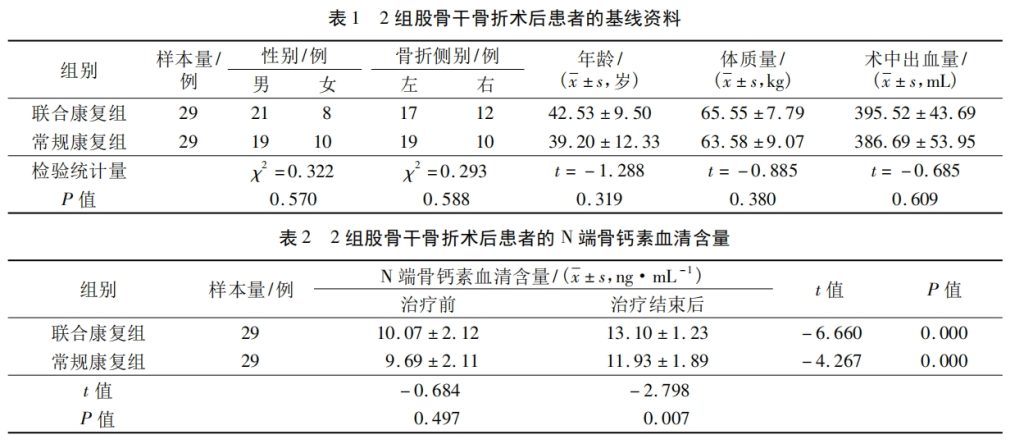
Patients with femoral shaft fracture who received compression plate and screw internal fixation at Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedic Hospital (Shenzhen Pingshan District Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital) from March 2020 to July 2022 were selected as the research subjects.
The 58 patients were numbered 1 to 58 in the order of enrollment, and the patient numbers were entered into an Excel spreadsheet. The RAND function in the Excel spreadsheet was used to generate 58 random numbers corresponding to the number of each patient. After the random numbers were sorted from small to large, the patients whose numbers corresponded to the first 29 random numbers were assigned to the conventional rehabilitation group, and the patients whose numbers corresponded to the last 29 random numbers were assigned to the combined rehabilitation group. Since the treatment methods used in the two groups were quite different, this study did not use the blind method.
The study included 49 patients undergoing knee surgery at knee and sports clinics. All agreed to participate and provided signed informed consent to perform timed Single Leg Stand (SLS) training on the floor at 1 week and were assigned to perform timed Single Leg Stand (SLS) training on the floor at 1 week. Anti-gravity treadmill group (AG) or control group, (CG) based on patient comfort. Those who experienced a “significant increase” in pain levels during the first balance test were placed in the anti-gravity treadmill group. Other subjects in the CG group who felt “comfortable” and had no or little pain or no or little pain experienced increased pain. Subjects in the anti-gravity treadmill group performed balance training on the treadmill every day for at least 5 days, with the pressure on the anti-gravity treadmill adjusted to painless or minimal pain a few days a week between the first and second balance tests. Minimum pain level at the beginning of each balance training session. Patients in the CG group performed balance training on the floor at least 5 days per week. During each balance exercise each day between balance tests, subjects were asked to stand on the surgical leg with the knee slightly bent, aiming to remain standing. 30 seconds. Repeat 3 times resting 30 seconds between each exercise.
Conventional rehabilitation group: The conventional rehabilitation group was treated with manipulation, exercise therapy and physical therapy after surgery. Manipulation therapy included tendon kneading, quadriceps stretching and relaxation, and knee flexion passive activity. Exercise therapy included trunk core muscle training, knee flexion and extension training, and proprioception training. Physical therapy was: 2 sets of interfering electricity from the SV-IT601D interferential electric therapy device were attached to the quadriceps, and the current intensity was set to 30 mA. Five times a week, 20 minutes each time, for a total of 4 weeks.
Combined rehabilitation group: After surgery, the combined rehabilitation group performed anti-gravity treadmill training on the basis of the intervention measures of the conventional rehabilitation group. The same therapist operated the Golden All anti-gravity treadmill training system (Tianjin Jinwanxiang Medical Equipment Co., Ltd.).
Patients put on sealed zipper pants before anti-gravity treadmill training. The therapist adjusts the height of the handles on both sides of the anti-gravity treadmill to be parallel to the patient’s greater trochanter of the femur, seals the zipper pants, starts to inflate and detect the patient’s weight, and sets the corresponding weight loss ratio according to the weight measured by the treadmill to start guiding the patient’s training. Patients can observe the movement status, stride, stride length on both sides and weight ratio of their lower limbs in real time on the screen, and make self-adjustments; therapists need to observe and guide the patient’s gait outside the transparent airbag, and remind the patient to keep up with the speed of the treadmill and adjust the stride in time.
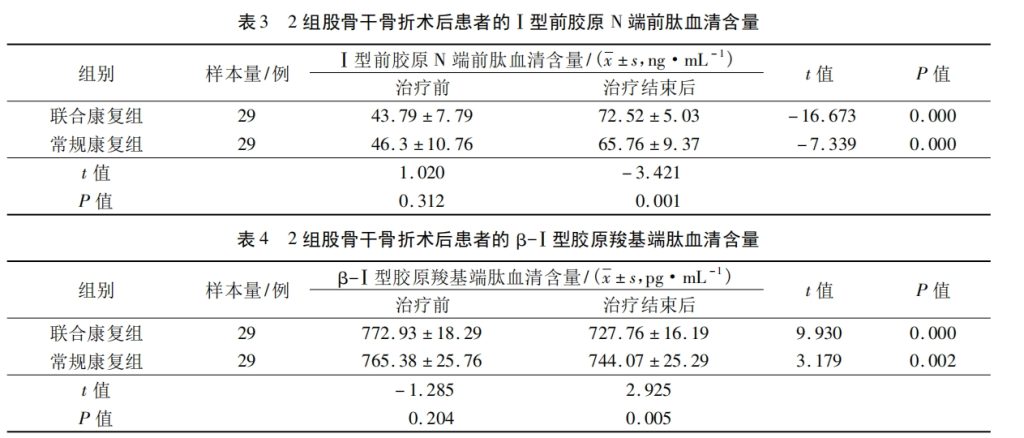
The results of this study showed that after the treatment, the levels of N-terminal osteocalcin and PINP in the serum of patients in the combined rehabilitation group and the conventional rehabilitation group were significantly increased compared with those before treatment, and the levels of N-terminal osteocalcin and PINP in the serum of the combined rehabilitation group were higher than those in the conventional rehabilitation group. This may be related to the fact that anti-gravity treadmill training stimulates bone cells to feel mechanical stress and increases the metabolic activity of osteoblasts.
Studies have confirmed that β-CTX shows a downward trend after femoral shaft fracture surgery, indicating good fracture healing. The results of this study showed that the serum β-CTX content of the two groups of patients was lower than that before treatment after treatment, and the serum β-CTX content of the combined rehabilitation group was lower than that of the conventional rehabilitation group, which suggests that anti-gravity treadmill training is beneficial to promote fracture healing. The results of this study show that the application of anti-gravity treadmill training in the rehabilitation treatment of femoral shaft fracture postoperative compression plate screw internal fixation can promote fracture healing and improve knee joint function.