Keywords: lower limb rehabilitation; postoperative rehabilitation; NASA Anti Gravity Treadmill
Abstract:
Objective: To explore the application value of anti-gravity treadmill training in the rehabilitation treatment of femoral shaft fracture after compression plate screw internal fixation. Methods: Fifty-eight patients with femoral shaft fracture who underwent compression plate screw internal fixation 4 weeks after surgery were randomly divided into a conventional rehabilitation group and a combined rehabilitation group, with 29 cases in each group. The conventional rehabilitation group received rehabilitation treatment with manipulation, exercise therapy and physical therapy, while the combined rehabilitation group received anti-gravity treadmill training on the basis of the intervention measures of the conventional rehabilitation group; both groups received treatment 5 times a week, 20 minutes each time, for a total of 4 weeks.
The article is cited in:
Application of anti-gravity treadmill training in rehabilitation treatment after compression plate and screw internal fixation of femoral shaft fracture
Femoral shaft fracture is one of the most common fractures in clinical practice, mostly caused by direct violence. After the fracture occurs, it is often accompanied by obvious local pain and swelling. Improper treatment of femoral shaft fractures can easily lead to fracture nonunion, knee joint dysfunction, etc. The focus of postoperative rehabilitation of femoral shaft fractures is to promote fracture healing and reduce the incidence of delayed fracture healing and nonunion. Studies have reported that appropriate stress stimulation is beneficial to promote fracture healing, thereby accelerating the patient’s rehabilitation process. However, the stress stimulation intensity and weight-bearing time required for the fracture ends of patients at different time periods after surgery are different. Conventional rehabilitation methods are difficult to control the time and intensity of weight-bearing, and cannot monitor the patient’s real-time gait data. The anti-gravity treadmill training system can monitor the patient’s weight-bearing intensity, time, gait data, etc. in real time, and realize weight-bearing walking under visual feedback of patients after fracture surgery, thereby achieving the purpose of increasing stress stimulation of the fracture ends. In order to explore the application value of anti-gravity treadmill training in the rehabilitation treatment of femoral shaft fractures after compression plate and screw internal fixation, we conducted this study, and now report as follows.
1 Clinical data
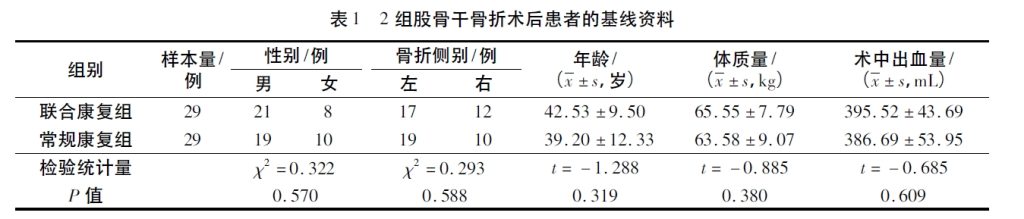
1.1 General data Patients with femoral shaft fracture who received compression plate screw internal fixation at Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedic Hospital (Shenzhen Pingshan District Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital) from March 2020 to July 2022 were selected as research subjects. The experimental plan was reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedic Hospital (Shenzhen Pingshan District Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital)
1.2 Inclusion criteria ① Meet the diagnostic criteria for femoral shaft fracture in “Surgery”; ② Unilateral femoral shaft fracture; ③ Compression plate screw internal fixation, 4 weeks after surgery, the operation was completed by the same group of doctors; ④ No loosening of internal fixation occurred after surgery; ⑤ Age 18 to 60 years old, regardless of gender; ⑥ Voluntary participation in this study and signing of informed consent.
1.3 Exclusion criteria ① Patients with severe cardiovascular, hepatic, renal, hematopoietic system and other diseases; ② Patients with fractures in other parts; ③ Patients with vascular and nerve injuries; ④ Patients with stenosis and deformity of the femoral shaft medullary cavity.
Conventional rehabilitation group The conventional rehabilitation group was treated with manipulation, exercise therapy and physical therapy after surgery. Manipulative therapy included Pingle Guoshi Rong muscle kneading method, quadriceps stretching and relaxation, and knee flexion passive activity. Exercise therapy included trunk core muscle training, knee flexion and extension training, and proprioception training. Physical therapy was: 2 sets of interferential electricity from the SV-IT601D interferential electricity therapy device were adsorbed on the quadriceps, and the current intensity was set to 30 mA. 5 times a week, 20 minutes each time, for a total of 4 weeks.
Combined rehabilitation group After surgery, combined rehabilitation was performed on the basis of the intervention measures of the conventional rehabilitation group. The same therapist operated the Golden All anti-gravity treadmill training system (Tianjin Jinwanxiang Medical Equipment Co., Ltd.). Before treadmill training, put on sealed zipper pants. The therapist adjusted the height of the handles on both sides of the anti-gravity treadmill to be parallel to the greater trochanter of the patient’s femur, sealed the zipper pants, and started to inflate and detect the patient’s weight. According to the weight measured by the treadmill, the corresponding weight loss ratio was set to start guiding the patient’s training. Treadmill training setting parameters: in the first week, subtract 75% to 80% of the patient’s own body weight, and the speed is 0 to 2 km·h-1; in the second week, subtract 65% to 75% of the patient’s own body weight, and the speed is 2 to 4 km·h-1; in the third week, subtract 55% to 65% of the patient’s own body weight, and the speed is 4 to 6 km·h-1; in the fourth week, subtract 45% to 55% of the patient’s own body weight, and the speed is 6 to 8 km·h-1. The slope of each weekly training is set to 0, and each training session lasts 20 minutes, 5 times a week. During training, patients can observe the movement status, stride, stride length on both sides, and weight ratio of their lower limbs in real time through the screen, and make self-adjustments; therapists need to observe and guide the patient’s gait outside the transparent airbag, and remind the patient to keep up with the speed of the treadmill and adjust the stride in time.
Conclusion:
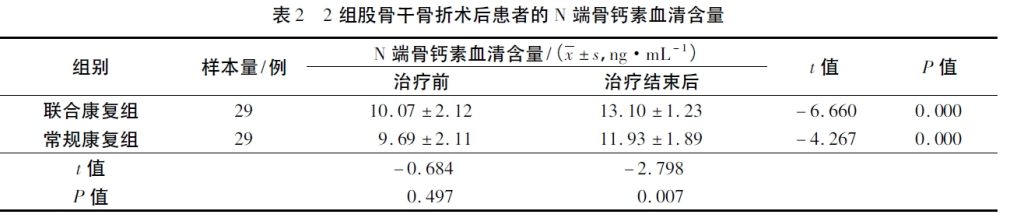
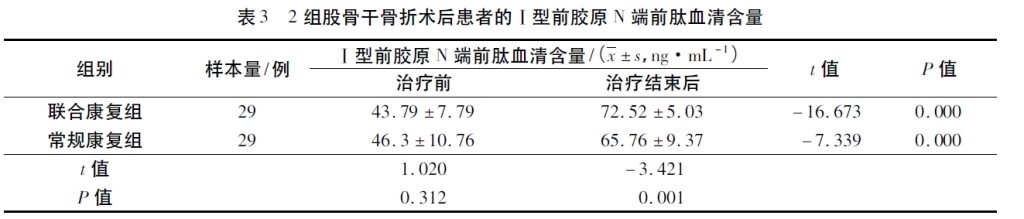
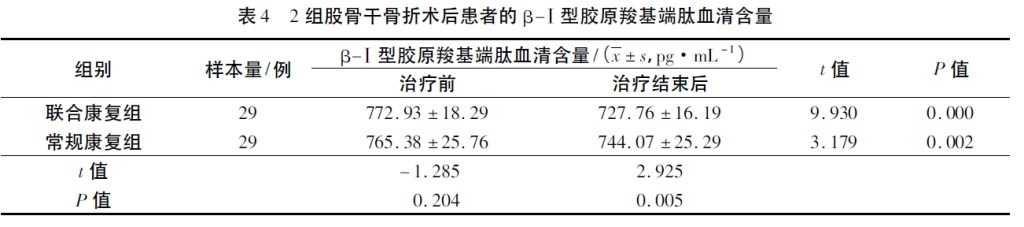
Studies have confirmed that β-CTX shows a downward trend after femoral shaft fracture surgery, indicating good fracture healing. The results of this study showed that the serum β-CTX content of the two groups of patients was lower than that before treatment after treatment, and the serum β-CTX content of the combined rehabilitation group was lower than that of the conventional rehabilitation group, which suggests that anti-gravity treadmill training is beneficial to promote fracture healing. The results of this study show that the application of anti-gravity treadmill training in the rehabilitation treatment after compression plate screw internal fixation of femoral shaft fracture can promote fracture healing and improve knee joint function.