Key words: Anti-gravity treadmill; stroke; walking ability;
Objective: To observe the application effect of the anti-gravity treadmill training system in the balance and walking training of elderly stroke patients.
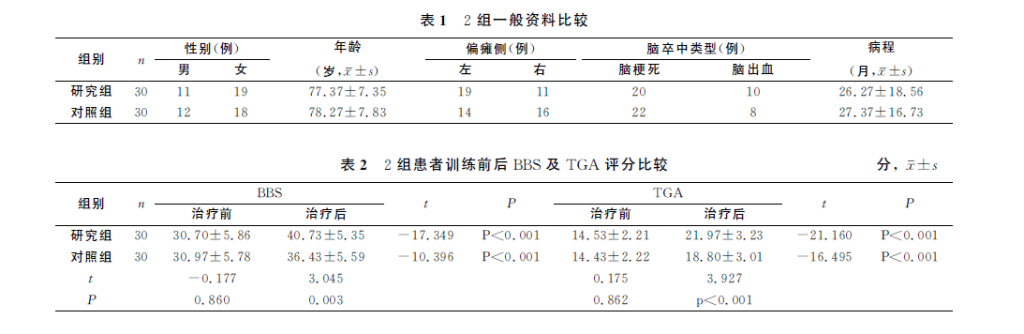
Methods: 60 elderly stroke inpatients in our hospital were selected and randomly divided into a research group and a control group, 30 cases each. Both groups received routine rehabilitation training and walking training, while the research group received anti-gravity treadmill walking training for 12 consecutive weeks. The Berg balance scale, Tinetti gait assessment scale, and 10m maximum walking speed test were used to evaluate the patients before and after treatment. Patient’s balance and walking ability.
Results: After 12 weeks of treatment, the BBS and TGA scores of both groups were significantly higher than before treatment (P<0.05), and the study group was higher than that of the control group (P<0.05); after treatment, the maximum walking speed of the two groups was higher than that before treatment. Each time point was significantly improved compared with before treatment (P<0.05), and the walking speed of the study group was significantly higher than that of the control group at 4 weeks, 8 weeks and 12 weeks of treatment (P<0.05).
Conclusion: The anti-gravity treadmill training system can effectively help improve the balance and walking ability of elderly stroke patients and is worthy of promotion and use.
Article cited in:[1]孔芳草,付丛会,李小通等.反重力跑台系统在老年脑卒中患者平衡及步行训练中的疗效[J].中国康复,2021,36(05):274-277.
Article link:反重力跑台系统在老年脑卒中患者平衡及步行训练中的疗效
In recent years, anti-gravity treadmill training system, as a new high-tech sports training method, has been gradually used in the field of rehabilitation medicine and attracted widespread attention. The anti-gravity treadmill is mainly composed of two parts: the treadmill system and the air pressure system. The treadmill system can adjust the speed and slope during exercise. The air pressure device can reduce the effect of gravity by adjusting the air pressure in the closed cabin. This is actually A kind of weight-reduction treadmill walking training can comprehensively train the patient’s weight-bearing, balance and stepping through partial weight loss and forced walking on the exercise treadmill, and improve the patient’s lower limb movement ability. At present, anti-gravity treadmills are mainly used in the field of sports rehabilitation, including lower limb sports injury rehabilitation and early stress weight-bearing training after orthopedic surgery, corrective training for changes in lower limb walking ability caused by peripheral nerve injury, aerobic training for obese patients, etc. About There are not many studies on its application in walking training for elderly stroke patients. This study uses an anti-gravity treadmill system to perform weight-loss walking training on elderly stroke patients, and observes the improvement effect on the patients’ balance ability and walking ability.
After a stroke, patients usually suffer from walking dysfunction due to reduced muscle strength of the lower limbs on the hemiplegic side, reduced balance ability, weakened proprioception, or abnormal patterns. The main manifestations include abnormal gait, slow walking speed, effort, and poor walking stability. . The reduction of walking ability greatly increases the risk of falling in daily activities, affecting patients’ mobility and quality of life. Therefore, the recovery of walking function after stroke has always been an important part of rehabilitation treatment. As age increases, the elderly’s body functions gradually decline, their physical strength declines, and various complications cause pain and discomfort, which makes patients reluctant to recover.
The training tolerance is low and it is difficult for elderly patients to complete high-intensity training every day. Compared with young stroke patients, walking training for elderly patients is more difficult and less effective. At present, elderly patients mostly stay at home or in nursing homes after becoming ill. They have low desire and demand to re-engage in social activities, and lack initiative in rehabilitation training. Some patients with walking ability rely on wheelchairs as a mobility tool for a long time, resulting in a gradual decrease in balance ability and loss of walking function. Weakened or even lost, resulting in disuse syndrome and increasing the burden on family members and caregivers.
In traditional walking rehabilitation training for stroke, the therapist uses various neurodevelopmental techniques to induce isolated movements of the joints of the lower limbs, and conducts individual intensive training on the patient’s lower limb weight-bearing, balance ability, stepping movements, center of gravity transfer, etc., and then exercises to relearn the pattern, training often requires the use of crutches and other assistive devices or in parallel bars. This conventional walking training is difficult to apply in elderly patients, is not safe, and does not significantly improve the patient’s balance and walking function. The anti-gravity treadmill system is actually a weight-reduced flat walking training. Studies have confirmed that weight loss walking training can effectively improve the walking ability of stroke patients compared with traditional walking training, and is more effective in increasing patients’ walking speed and improving step length symmetry. Walking speed is an objective index that can comprehensively reflect the entire process of changes in the elderly’s physical activity and walking ability recovery after stroke. When the treadmill is moving, the conveyor belt forces the patient to automatically coordinate the muscles of the lower limbs to continuously complete voluntary movements such as stepping forward, forming a task training that strengthens the stepping of the affected lower limb. At the same time, the therapist continuously speeds up the treadmill walking speed according to the patient’s recovery condition. When the mandatory limit is reached, Training intensity and repetition frequency can effectively activate the remodeling of the cortical motor area around the injured area of the training site, promote compensation, reorganization and functional recovery of the central nervous system, thereby overcoming the learned disuse of the affected lower limb and improving walking ability. Abnormal gait after stroke may be one of the important reasons for the significant decrease in walking speed of patients. During the walking training process, it often happens that after the patient is trained on weight-bearing, balance, stride and other walking elements, the patient is found to have a slow walking speed and obvious abnormal gait when walking. This may be due to the patient’s inability to use the previous skills in a real and complex walking environment. Effective combination of component training results makes it difficult to complete a relatively complete and continuous walking cycle. At the end of the support phase of the affected side, the treadmill conveyor belt passively hyperextends the hip flexors and gastrocnemius muscles, causing muscle contraction, thereby generating power for hip flexion and ankle plantar flexion, speeding up the forward swing of the affected limb and shortening the affected leg. The support time of the lower limb on the unaffected side when stepping helps to correct the asymmetry of gait; the anti-gravity treadmill system combines the three elements of walking (weight-bearing, balance, and stepping) for comprehensive training. Compared with traditional walking training methods, it pays more attention to both sides. Continuous training of lower limb coordination and walking. The results of this study show that after 12 weeks of treatment, the TGA score and maximum walking speed of the study group were significantly improved compared with before treatment, and the improvement was significantly better than that of the control group. The data showed that the patient’s maximum Walking speed recovery continues to improve with the extension of training time. It shows that anti-gravity treadmill training can improve the gait of patients with hemiplegia and improve their walking ability.
Speed plays a significant role.
The main purpose of lower limb rehabilitation for elderly stroke patients is to improve motor function and physical strength, enhance balance ability, and prevent and reduce falls. The results of this study showed that the balance ability of the study group improved significantly better than that of the control group. In traditional rehabilitation treatment, elderly patients often fear walking training due to fear of falling. Therefore, safety should be considered when designing training programs for elderly patients. Improving patients’ psychological support is conducive to the development of rehabilitation training. The anti-gravity treadmill system performs lower limb training in a closed air bag, which reduces the risk of falls in elderly patients during walking training. Compared with traditional walking, patients feel less fatigue and can carry out continuous training, which increases the safety of the experiment and the patients. compliance; at the same time, the low-gravity environment can support the patient’s weight, reduce the load on the affected lower limb, and greatly reduce the difficulty of walking. The patient can better control and maintain trunk stability during the transfer of the center of gravity from the unaffected lower limb to the affected lower limb. , which has a positive effect on improving its dynamic balance ability.
In conclusion, the use of anti-gravity treadmill for weight loss walking training can help improve the balance and walking ability of elderly stroke patients. This is consistent with the research results of Wang Wenqing et al. It needs to be emphasized that anti-gravity treadmill training We should still pay attention to the importance of routine rehabilitation in the early stage and strengthen the training of the patient’s lower limb function. In the later stage, combined use of anti-gravity treadmills may achieve better results. The rehabilitation of elderly stroke patients is relatively long-term, slow and complicated. How to design a reasonable and personalized treatment plan suitable for elderly patients, optimize the treatment effect and prolong the benefit period of patients in their long-term life in the future remains to be further studied.